Please follow 2 steps below to resolve slow/frozen server issues if CPU/RAM/Storage does not reach the limit and network has no packet losses
Step 1: Disable bitmap caching and reduce broadband speed.
If the cache fills up with too many images, it can become overloaded and slow down the process of retrieving and combining them.
This can lead to delays and temporary freezing of the remote screen. Also, Bitmap caching requires adequate memory on the client device. If memory runs low, it can struggle to manage the cache efficiently, leading to performance issues and potential freezing.
This section will guide you on how to disable this option in Windows Remote Desktop Connection.
1. Search and Open Remote Desktop Connection or mstsc on your local computer.

2. Once Remote Desktop Connection is open, click on Show Options.
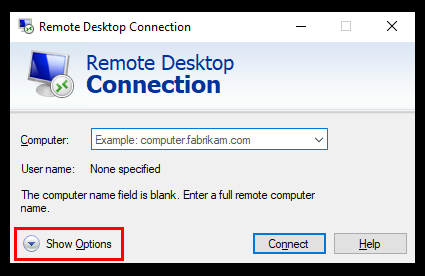
3. Next, navigate to the Experience tab.
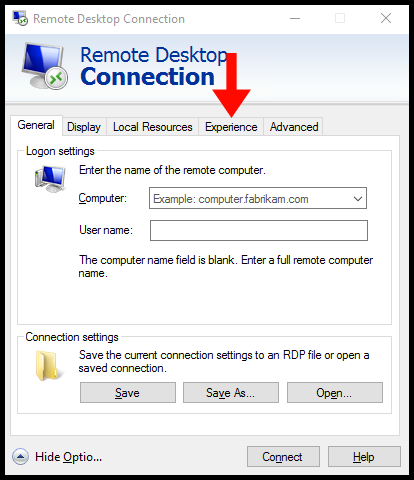
4. Select “Low-speed broadband” from Performance and Uncheck the option Persistent bitmap caching.
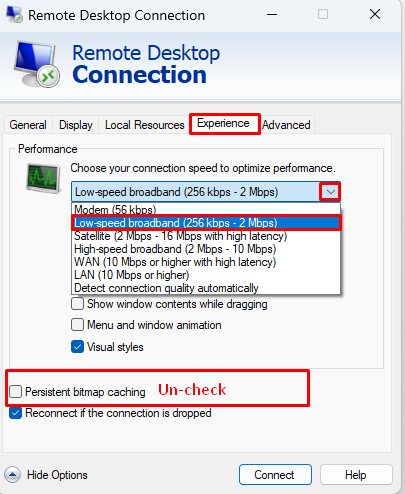
5. Finally, try to connect to the RDP by clicking on the Connect button.
Step 2: Disable UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
UDP prioritizes speed over reliability, so it can lose or misorder data packets during transmission, which disrupts the consistent data flow RDP needs for seamless screen updates and user interactions, leading to lag or freezing. To ensure reliability, consider disabling UDP and using TCP. Please follow the following steps to disable UDP.
1: Open Local Group Policy Editor in your Windows server
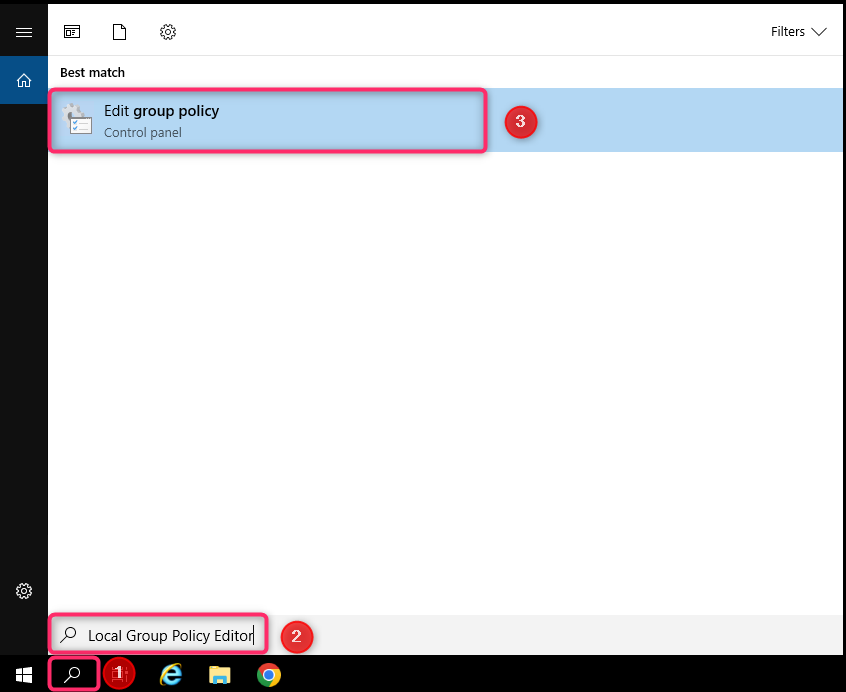
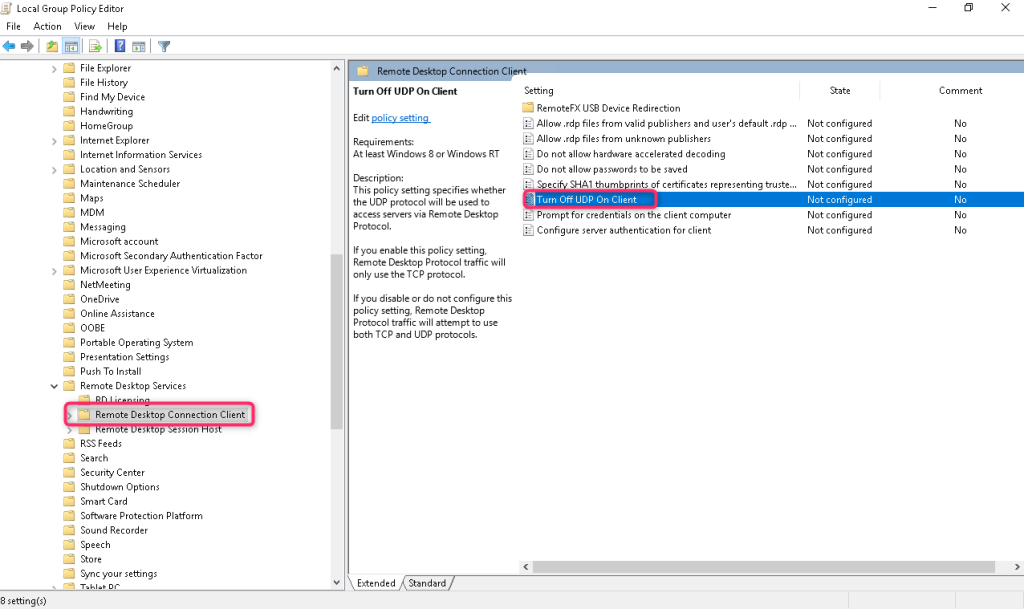
2. Go to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Connection Client.
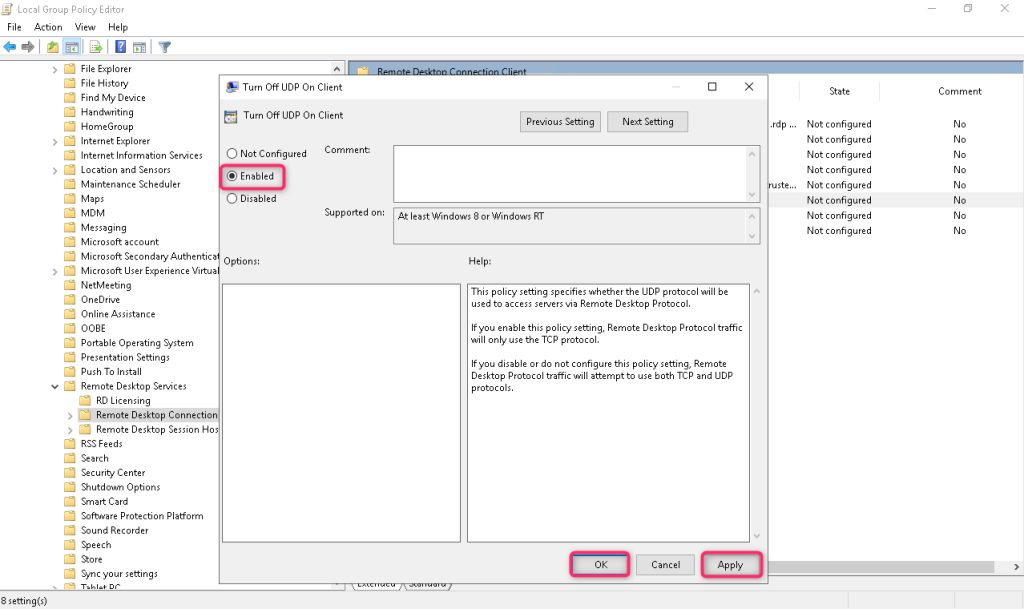
Find the Turn Off UDP On Client option and set it to Enabled.
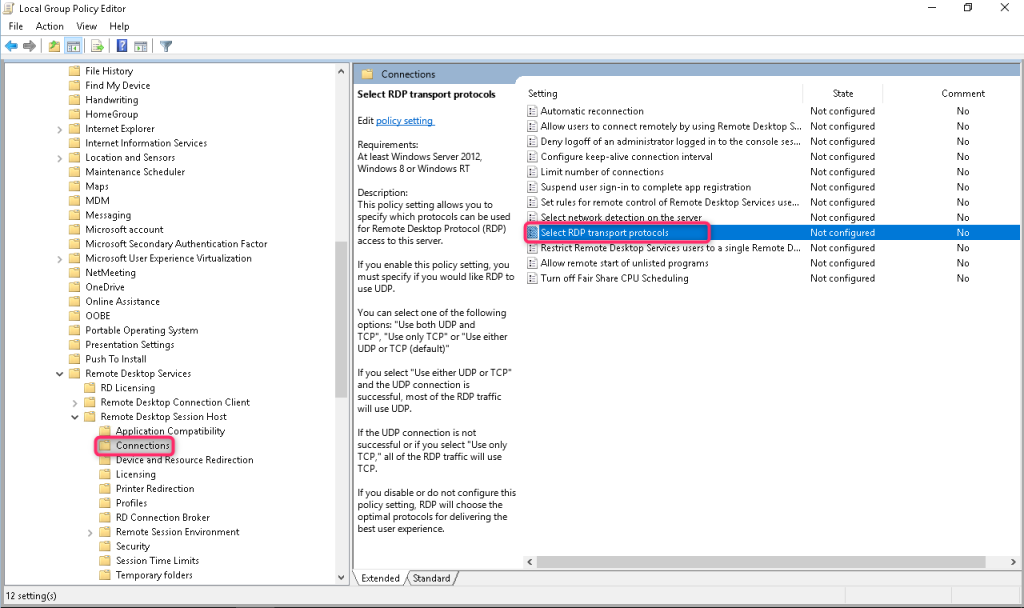
3. Go to “Computer Configuration” -> “Administrative Templates” -> “Windows Components” -> “Remote Desktop Services” -> “Remote Desktop Session Host” -> “Connections”
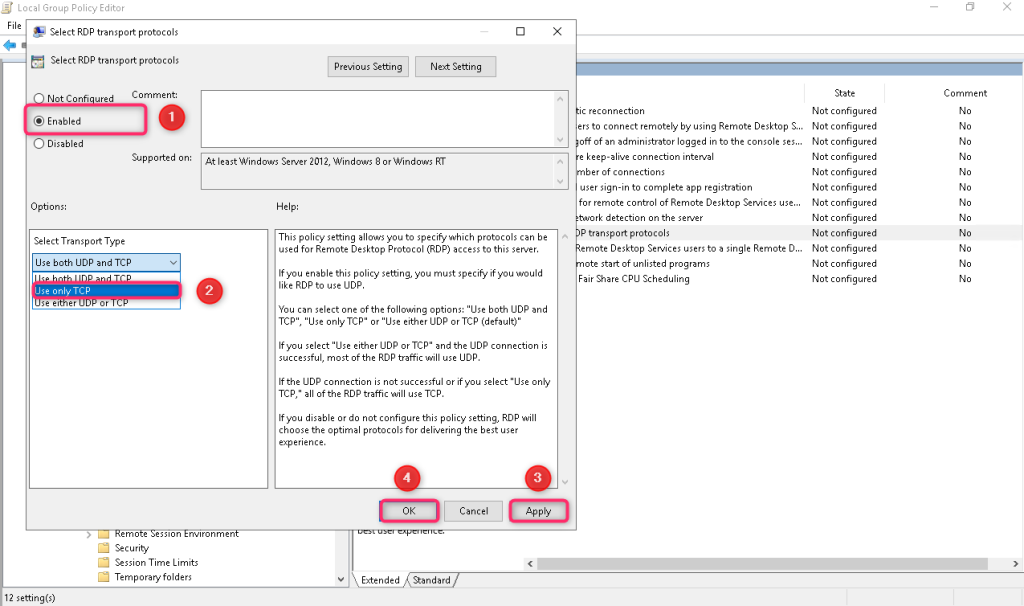
Find the Select RDP Transport Protocols option and set it to Enabled, and in the options select Use only TCP.
4. Restart your server and reconnect to your server.
